Global urbanisation and population growth has massively increased the amount of waste produced causing waste generation to surge exponentially. Let’s discuss about 5 Types of Waste. In fact, some estimates suggest it will double by 2025. Add to this the fact the problem of waste being hazardous to people’s health and the environment if it is improperly treated, stored, transported, or disposed of and the role waste companies play in dealing with waste becomes increasingly important.
To help waste management companies deal with your business waste, it is first necessary to understand what type of waste your company produces to ensure it is disposed of correctly. Waste generally falls into the following categories each of which will be disposed of in different ways, depending on how hazardous or indeed how useful that waste is and the potential environmental impact if it is not disposed of correctly.
1. Solid Waste
Solid waste is a term that refers to waste material that is solid in nature. This can include waste generated through either domestic, commercial, or other activities producing levels of waste that can be described as solid. Solid waste can include waste from construction or demolition sites, industrial or automotive businesses where waste is produced in large volumes or is hazardous.
Solid waste generally falls into the following types:
- Cardboard and paper – This can be recycled.
- Plastic – Most plastic waste isn’t usually biodegradable, which is why it is separated from general rubbish.
- Metal and Cans – A type of solid waste which can be easily be recycled.
- Ceramic and Glass Waste – These can be recycled but doing so requires waste to be heat treated.
- Industrial waste such as electrical components, metals and so on.
At a domestic level the above types of waste are usually collected by the local authority, however businesses may require the services of a commercial waste management company to ensure larger quantities of solid waste are dealt with according to environmental regulations.

2. Hazardous Waste
Hazardous waste can come in solid or liquid form and if not disposed of correctly it can have grave consequences for both people and the environment. Even some household products can ignite, react or explode under certain circumstances which is why it is illegal to throw hazardous waste away in the waste bin, or down the drain into sewers. It is essential therefore to understand the types of waste that can fall under the banner of hazardous.
Examples of chemicals and solid waste that can fall into the hazardous waste category include:
- Paints
- Clinical Waste
- Cleaners
- Oils
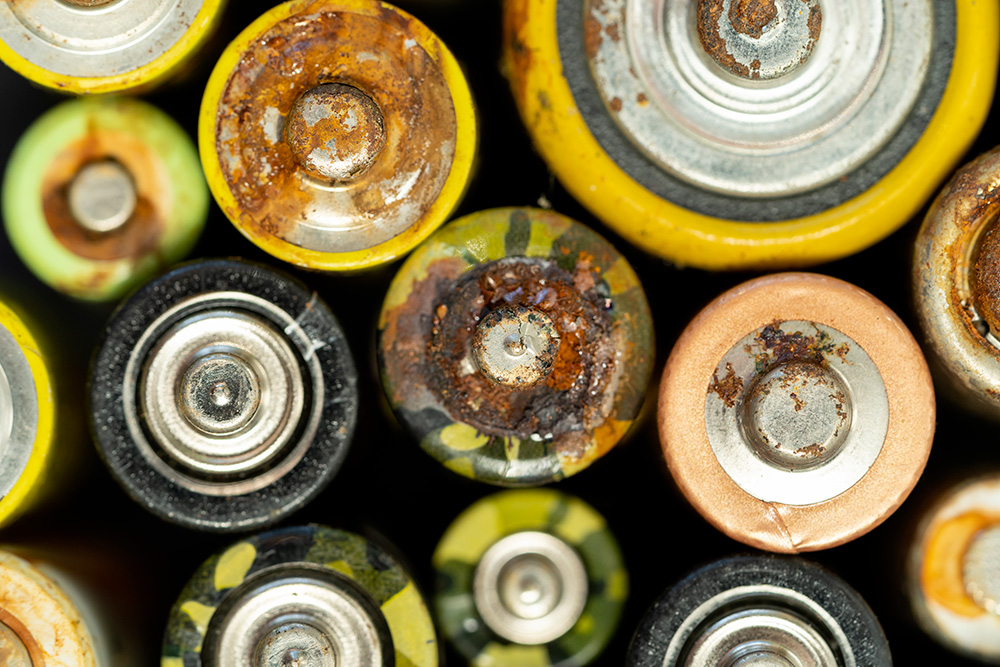
- Batteries
- Pesticides
- Automotive fluids
- Asbestos

3. Biodegradable Waste
Biodegradable waste is a term used for waste that can be broken down by bacteria and other organisms and often disposed of either through composting, landfill, or incineration. Types of biodegradable waste include:
- Garden waste
- Foods including vegetables, fruit peels,
- Paper and other organic materials such as
- Animal excrement
- Human waste
Even if waste is bio-degradable, this doesn’t mean it can’t be harmful to the environment. For example invasive plants such as Japanese Knotweed can cause huge problems if it is not disposed of correctly while animal excrement can also have detrimental effects on the environment.

Recycling and containing biodegradable waste is the most effective way to reduce its impact on the environment and the planet. Biodegradable waste produces methane which is a warming gas that is a more potent greenhouse gas than CO2.
4. Industrial Waste
British industries generate and dispose of approximately 43.9 million tons of industrial waste each year. If industrial waste is not handled and disposed of properly, it can pose a risk to the environment. Thankfully, there are ways to dispose of industrial waste which reduce the impact on the environment. Companies can reduce and even recycle industrial waste instead of adding to the burden on the UK’s landfill sites.
Industrial waste disposal companies can guarantee compliance with regulations and proper disposal. They offer services such as transportation to disposal sites – helping your company save both time and money in the long run by adhering to local authority and other regulations.
Types of industrial waste include:
- Toxic/ Hazardous waste – by-products of manufacturing that can be harmful if not disposed of correctly.
- Chemical waste – liquid waste including acids, alkalis, cleaning agents and oil.
- Solid waste – Animal feed, electronic waste, glass and ceramic waste.
- Paper products – Paper mills, waste from printing companies
- Radioactive waste – This requires specialist waste removal services
- Metal waste – Produced in manufacturing processes. This can often be melted down and recycled.
- Fuel and lubricants – Again used in manufacturing which require specialist removal and waste processing.
- Drums, containers– used for chemical storage which can sometimes be recycled or put to alternative uses.

5. Agricultural Waste
Agricultural waste can be disposed of in several ways. Anaerobic digestion, thermo-chemical conversion, and anaerobic or aerobic treatment lagoons are among the options. These methods can be utilised to transform agricultural waste into energy resources, bedding, mulch, organic matter and plant nutrients. Proper management of these materials can minimize the environmental impact and help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Types of agricultural waste include:
- Manure and slurries waste – over 90% of farm waste falls into this category according to government figures. This is often used as fertilizer.
- Old machinery
- Pesticide containers – Agricultural chemical containers can be disposed of in authorised disposal sites.
- Tyres
- Batteries
Waste producing households, businesses and organisations all have a responsibility to ensure that waste is properly sorted to reduce its impact on the environment. While waste companies play a vital part in processing waste, it is also important that everyone takes responsibility for their waste and ensure it is disposed of in the correct way to reduce its impact on the planet.